Left to right: Pegasus, Taurus, Minotaur I, Minotaur II, Minotaur III, Minotaur IV, Minotaur V, Antares, Human figure for scale (1.8m tall).
Rockets of Orbital Sciences Corporation (Now part of Northrop Grumman)
Pegasus Rocket
Pegasus is an air launched space launch vehicle. All three stages use Orion solid motors.
Pegasus first flew in 1990. An improved model, known as Pegasus XL, started flying in 1994. The XL model features lengthened first and second stage motors.
Most missions are launched from beneath a modified Lockheed L-1011 aircraft. Early missions were launched from a B-52 Stratofortress.

Pegasus-XL Rocket Stages
First Stage
Pegasus XL uses an Orion 50S XL as its first stage. The 50S XL has a fixed nozzle.
Second Stage
Second stage is an Orion 50XL.
Third Stage
An Orion 38 serves as third stage. The Orion 38 includes a vectorable thrust nozzle.
Pegasus-XL
Pegasus-XL on display at the Udvar-Hazy center. (Photos: Richard Kruse, 2008)






Taurus
The Taurus is a four-stage, all solid propelled launch vehicle.
Taurus has flown nine missions between 1994 and 2011. Three of the nine launches failed.
The rockets third and fourth stages are similar to those used with the Pegasus launch vehicle.

Taurus Rocket Stages
Illustration showing typical Taurus stages. Actual configurations vary depending on requirements.
First Stage (Stage 0)
The Taurus typically uses a Castor-120 as its first stage. On some models, a Peacekeeper first stage is used.
Second Stage (Stage 1)
Second stage can be either an Orion 50ST or 50SXLT. Both models feature a vectorable thrust nozzle.
Third Stage (Stage 2)
The third stage is an Orion 50T or Orion 50XLT. Both models feature a vectorable thrust nozzle.
Fourth Stage (Stage 3)
An Orion 38 serves as fourth stage. The Orion 38 includes a vectorable thrust nozzle.
Minotaur
Minotaur Space Launch Vehicles
Operated by Orbital Sciences Corporation, the Minotaur series of launchers are derived from Minuteman and Peacekeeper intercontinental ballistic missile hardware.
For more information, visit the Orbital website.
Minotaur I
Minotaur I is an all solid fueled, four stage space launcher. The first and second stages were formally used with the Minuteman ICBM.
The rockets third and fourth stages are similar to those used with the Pegasus launch vehicle.
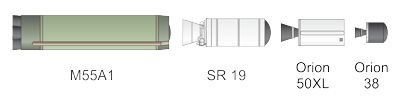
Minotaur I Rocket Stages
First Stage
First stage of the Minotaur rocket is a refurbished Minuteman II M55A1 solid rocket motor. The four nozzles are gimbaled to provide thrust vector control.
Second Stage
A refurbished Minuteman SR-19 solid rocket motor serves as second stage. The SR-19 features thrust vector control using liquid injection. Roll control is provided by a hot gas system.
Third Stage
Third stage is an Orion 50XL. Built by ATK, the 50XL features a vectorable nozzle.
Fourth Stage
An ATK Orion 38 serves as the fourth stage. The motor has a vectorable nozzle.
Minuteman III ICBM
Minuteman III on display at the National Air and Space Museum. (Photos: Richard Kruse, 2008)








Minotaur II
Minotaur II is a sub-orbital target vehicle launcher. The rocket uses the first three stages from former Minuteman II ballistic missiles.
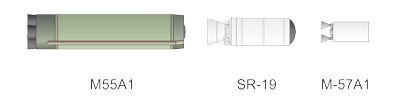
Minotaur II Rocket Stages
Minotaur III
The Minotaur III is intended for suborbital launches and uses the first three stages of decommissioned PeaceKeeper (MX) ballistic missiles. A hydrazine fueled fourth stage is included.
Minotaur IV
The Minotaur IV's first three stages were formally used with the PeaceKeeper (MX) ballistic missile.
The Minotaur IV first flew in April 2010.
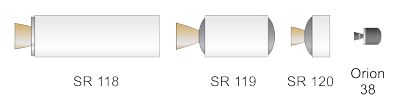
Minotaur IV Rocket Stages
First Stage
First stage of the Minotaur IV is a SR-118 solid rocket motor.
Second Stage
Second stage is a refurbished SR-119 motor.
Third Stage
An SR-120 motor serves as third stage.
Fourth Stage
Fourth stage is typically an Orion 38 solid rocket motor. A Star 48BV may also be used if required.
Minotaur V
The Minotaur V is a five stage version of the Minotaur IV. The first three stages were formally used with the Peacekeeper (MX) ballistic missile.
The first Minotaur V mission sucessfully placed the LADEE spacecraft into orbit. The launch took place on 6 September 2013 from NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.

Minotaur V Rocket Stages
First Stage
First stage of the Minotaur V is an SR-118 solid rocket motor.
Second Stage
Second stage is a refurbished SR-119 motor.
Third Stage
An SR-120 motor serves as third stage.
Fourth Stage
Fourth stage is a STAR 48BV solid rocket motor.
Fifth Stage
The rockets fifth stage is a STAR 37FM solid rocket motor.
Antares

Cygnus Spacecraft
The Cygnus spacecraft is designed as a re-supply vehicle for the International Space Station.
Developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation, the Antares rocket conducted its maiden flight in April 2013. The rocket was launched from the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport, located near NASA's Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia.
First Stage
Early first stages (100 series) were powered by a pair of AJ26 engines. The AJ26 engines were modified Russian NK-33 engines. Later missions (200 series) used Russian RD-181 engines. Both engines use RP-1 and liquid oxygen as propellants.
Second Stage
The second stage initially used a solid-fueled Castor 30A motor. Later missions used the Castor 30B or Castor 30XL motor.
Third Stage
Future missions may optionally use a STAR-48 based, solid-fueled third stage motor.
Cygnus
A regular payload for the Antares rocket is the Cygnus spacecraft. Cygnus was developed to ferry supplies to the International Space Station. Known as CRS, or commercial resupply missions, these flights are scheduled to occur around twice per year.
| Flight | Launch Date | Launch Site | Ver. | Primary Payload | Mission | Results |
| 9 | 17 Nov 2018 | MARS | 230 | Cygnus | CRS NG-10, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 8 | 21 May 2018 | MARS | 230 | Cygnus | CRS OA-9, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 7 | 12 Nov 2017 | MARS | 230 | Cygnus | CRS OA-8E, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 6 | 17 Oct 2016 | MARS | 230 | Cygnus | CRS OA-5, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 5 | 28 Oct 2014 | MARS | 130 | Cygnus | CRS Orb-3, Resupply of ISS. | Failure |
| 4 | 13 Jul 2014 | MARS | 120 | Cygnus | CRS Orb-2, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 3 | 9 Jan 2014 | MARS | 120 | Cygnus | CRS Orb-1, Resupply of ISS. | Success |
| 2 | 18 Sep 2013 | MARS | 110 | Cygnus | Orb-D1, First Cygnus berthing with ISS. | Success |
| 1 | 21 Apr 2013 | MARS | 110 | Mass Simulator | Test flight of Antares rocket. | Success |
NOTE: MARS = Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport.
More information about Antares, can be found at the Northrop Grumman website.
 Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.


