Mariner Program
Overview of the Mariner Program
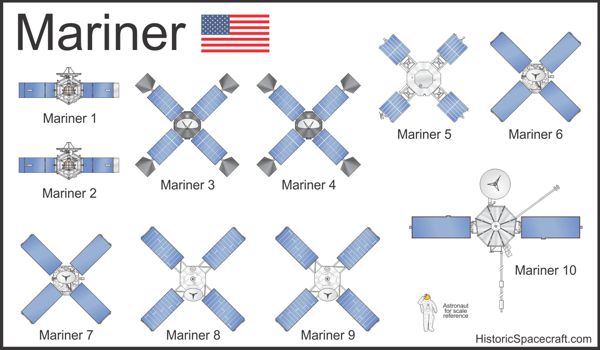
The Mariner program consisted of ten exploration probes launched between 1962 and 1973. The spacecraft were designed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory to investigate the planets Mars, Venus, and Mercury.
All Mariner missions were launched on Atlas rockets, with early missions using Atlas-Agena, and later missions using Atlas-Centaur. Because of reliability issues with available launchers, the missions tended to use pairs of spacecraft launched on separate rockets. Ultimately three Mariner missions failed due to launch vehicle or payload shroud failures. In each case, the duplicate spacecraft was able to complete the mission.
Mariner spacecraft accomplished a number of important firsts, including the first mission to visit Venus (Mariner 2), the first successful Mars encounter (Mariner 4), and the first mission to visit Mercury (Mariner 10).

Mariner 1 & 2 (Venus Flyby)

Mariner 2
Mission
Mariner 1 & 2 were designed to conduct flybys of the planet Venus. Each spacecraft was launched on an Atlas Agena-B rocket (right)
The spacecraft's electronics were contained in a hexagonal base, measuring 1.04 m across and .36 m tall. A pyramid shaped structure, supporting some of the scientific instruments, was mounted on top of the hexagonal base. Two solar panels, .76 m wide and with a total span of 5.05 m, provided electrical power. A high gain directional dish antenna, mounted below the hexagonal base, was used for communications with Earth. A cylindrical omni-directional antenna was mounted on top of the pyramid structure. A monopropellant propulsion system was used for midcourse maneuvers.
Experiments included a microwave radiometer, an infrared radiometer, a magnetometer, a cosmic ray detector, a cosmic dust detector, a solar plasma spectrometer, a particle detector, and a celestial mechanics experiment.
Mariner 1
Mariner 1 was destroyed in a launch vehicle failure on 22 July 1962. The Atlas-Agena rocket veered off course and had to be destroyed by the range safety officer.
Mariner 2
Launched on 27 August 1962, Mariner 2 was the first spacecraft to visit Venus. The spacecraft was launched from complex 12 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Closest approach to Venus, 34,773 km, occurred on 14 December 1962.
Mariner 2 Replica
These photos are of a replica, constructed from test components, on display at the National Air and Space Museum. (Photos: Richard Kruse, 2009)





Mariner 3 & 4 (Mars Flyby)
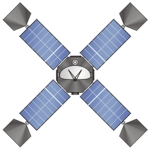
Mariner 4
Mission
Mariner 3 & 4 were intended to conduct flybys of the planet Mars. Each spacecraft was launched on an Atlas-Agena D rocket (right).
Mariner 3
Mariner 3 was launched on 5 November 1964. A launch shroud failed to separate and the spacecraft was not placed on the correct trajectory.
Mariner 4
Mariner 4 was launched on 28 November 1964. The spacecraft successfully flew by Mars on 14 July 1965. The mission returned the first close-up images of another planets surface.

Mariner 5 (Venus Flyby)
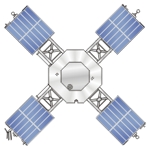
Mariner 5
Mariner 5 was launched on 14 June 1967, on an Atlas Agena-D rocket (right), from launch complex 12 at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. Closest approach to Venus, around 4,000 km, occurred on 19 October 1967.
The spacecraft was built as a backup for the Mariner 4 Mars probe. After the success of Mariner 4, the Mariner 5 spacecraft was reconfigured for a Venus flyby.
Mariner 5 experiments included an interplanetary ion plasma probe, a trapped radiation detector, a triaxial low field helium magnetometer, an ultraviolet photometer, a two-frequency beacon receiver experiment, an S-band occultation experiment, and a celestial mechanics experiment.

Mariner 6 & 7 (Mars Flyby)

Mariner 6
Mission
Mariner 6 & 7 were intended to conduct flybys of the planet Mars. Each spacecraft was launched on an Atlas-Centaur rocket (right).
Mariner 6
Mariner 6 (Mariner F), was launched on 24 February 1969. The spacecraft successfully flew by Mars in July 1969. The mission returned images of the Martian surface.
Mariner 7
Mariner 7 (Mariner G) was launched on 27 March 1969. The spacecraft successfully flew by Mars in August 1969. The mission returned images of the Martian surface.

Mariner 8 & 9 (Mars Orbiters)

Mariner 9
Mission
Mariner 8 & 9, sometimes known as "Mariner Mars 71", were intended to become the first spacecraft to enter orbit around the planet Mars. Each spacecraft was launched on an Atlas-Centaur SLV-3C rocket (right).
Mariner 8
Mariner 8 (Mariner H) was launched on 8 May 1971. A failure with the Centaur upper stage resulted in the spacecraft falling back to Earth.
Mariner 9
Mariner 9 (Mariner I) was launched on 30 May 1971. The spacecraft successfully entered orbit around Mars in November 1971. The successful mission returned thousands of images of the Martian surface.

Mariner 10 (Flybys of Venus and Mercury)
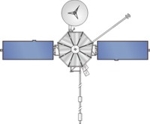
Mariner 10
Launched on 3 November 1973, Mariner 10 conducted flybys of both Venus and Mercury, becoming the first spacecraft to visit two planets. The spacecraft was launched on an Atlas Centaur rocket (right), from launch complex 36B at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station. The Venus flyby, with a closest approach of 5,768 km, occurred on 5 February 1974. A total of three Mercury flybys were conducted, occurring on 29 March 1974, 21 September 1974, and 16 March 1975.
Mariner 10 Flight Spare
These photos are of the Mariner 10 backup spacecraft, on display at the Udvar-Hazy Center. (Photos: Richard Kruse, 2009)








References
NASA Facts, Mariner to Mercury, Venus and Mars (PDF), Jet Propulsion Laboratory.
Mariner-Venus 1962: Final Project Report (PDF), NASA SP-59. 1965.
To Mars: The Odyssey of Mariner IV (PDF), JPL Technical Memorandum NO. 33-229. 1965.
J. A. Dunne and E. Burgess, The Voyage of Mariner 10 (PDF), Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 1978.
 Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.



















 Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.
Images by Richard Kruse are licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial 3.0 United States License.